Who is customer success manager
Cross-Selling vs. Upselling: Expanding the Value Proposition
- What Is Cross-Selling?

- What Is Upselling?

- How Do I Implement Upselling and Cross-Selling?

HubSpot’s 2024 State of Sales Report — which prompted opinions of more than 1,400 professionals across three continents — has found that the average share of revenue generated as a result of upselling activities stands at 21%. In the same way, numbers-wise, cross-selling amounts to 21% of all earnings produced by respondents’ organizations on average.
In this article, we describe the concepts of upselling and cross-selling, discuss the pros and cons of each, and suggest a tool to help you embrace these tactics.
What Is Cross-Selling?
Cross-selling is essentially about offering additional products or services to an existing customer. Think of it as building on an already established relationship. Instead of focusing solely on the initial product or service, you identify complementary offerings that can help ensure you follow all the freshest customer experience trends and address newly emerged needs.
Impact of Cross-Selling: A Metric-Driven Perspective
This tactic can significantly influence your business’s bottom line by positively impacting several key performance indicators.
- Average Order Value (AOV) is a direct beneficiary of cross-selling. Once you introduce complementary products or services to a customer’s initial purchase, you can substantially increase the total value of each transaction. For instance, someone buying a brand-new laptop might also consider items like a protective case, a productivity software suite, or an extended warranty. These additional items contribute directly to a higher average order value.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is another metric that sees a boost from cross-selling. When a customer is satisfied with a primary purchase and is presented with relevant and valuable extras, they are more likely to continue doing business with the company. This repeated engagement and increased spending over time contribute to a higher customer lifetime value. For example, a customer who initially purchases a cloud storage plan might be cross-sold advanced encryption mechanisms protecting that storage, leading to increased revenue over time.
- Customer Retention Rate (CRR) benefits significantly from cross-selling efforts, too. When providing products or services that solve unaddressed needs, you can strengthen customer loyalty and reduce churn. A fintech company, for example, might cross-sell investment services to customers who have been using its savings account for a while, deepening the relationship and decreasing the probability of switching to a rival.
- Finally, Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) is no exception to being positively impacted by effective cross-selling. When customers perceive that cross-sell recommendations are genuinely helpful and relevant to their needs, it enhances their overall experience. This positive perception translates to higher customer satisfaction scores. A software company, for instance, might offer next-step training or support services to customers who have recently purchased a new product, demonstrating a commitment to their success and satisfaction.
The Downside of Cross-Selling
While cross-selling can yield significant benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge its potential drawbacks. When not executed effectively, cross-selling can have detrimental consequences.
Reduced trust is a significant risk. If customers perceive cross-selling as overly aggressive or manipulative, their trust in the company can erode. For instance, persistently offering irrelevant or low-quality products can create the impression that the business is more interested in profit than customer satisfaction.
Customer dissatisfaction is another potential outcome. If cross-sold products or services fail to meet customer expectations or solve their problems, it can lead to frustration and disappointment. A classic example is recommending a product that is incompatible with the customer’s existing setup.
A lower likelihood of future engagement is a direct consequence of customer dissatisfaction. When customers have unpleasant experiences with cross-selling, they are less likely to make future purchases or recommend the company to others. The result? A decline in customer loyalty and a damaging impact on the company’s reputation.
Profit loss might seem counter-intuitive, but ineffective cross-selling can actually cause it. The expenses related to unsuccessful cross-selling attempts can outweigh the revenue generated. In other words, the loss of customers due to negativity can result in significant longer-term profit declines.
To mitigate these risks, you must adopt a customer-centric approach, ensuring that cross-selling recommendations are genuinely valuable and relevant to the customer’s needs.
What Is Upselling?
In plain English, upselling is about upgrading the potential customer’s (learn more about lead vs. prospect vs. opportunity) initial choice to a more premium option.
For instance, a software development firm might initially propose a basic web application development project. Upon further research into customer’s pain points, the sales team could spot opportunities to upsell by suggesting a reliever package that includes additional features, such as payment processing integration, mobile app development, or advanced analytics capabilities.
Tipping the Scales of LTV: The Upselling Advantage
Upselling is another direct path to increased revenue. Having persuaded customers to purchase a higher-tier product, you can significantly boost your average order value. In turn, that would translate into higher overall sales without the need to acquire new customers. For instance, a software development firm might upsell a customer from a basic license to a premium version with advanced functionalities, resulting in a substantial increase in revenue per customer.
Speaking of new customer acquisition, it’s often expensive and time-consuming. Upselling focuses on converting existing customers into higher-paying ones, which significantly reduces customer acquisition costs. By nurturing relationships with current customers and offering them upgraded options, you can maximize the return on investment from your existing customer base.
Moreover, by offering products or services that better align with a customer’s needs, your business can provide greater value. For example, a customer purchasing a basic website might be introduced to a more sophisticated e-commerce platform that can drive sales and growth, with that added value leading to increased customer loyalty and even advocacy.
Tread Carefully
Upselling, while a powerful revenue driver, carries inherent risks.
Effective upselling requires a shift from a traditional sales approach to a consultative one. If sales representatives focus solely on pushing products without understanding the customer’s specific needs, they risk alienating potential buyers. A consultative approach, on the other hand, builds trust and positions the salesperson as a trusted advisor, increasing the likelihood of a successful upsell.
A deep understanding of the product or service is crucial for effective upselling. Without this knowledge, salespeople may struggle to articulate the value proposition of higher-tier offerings or to address customer concerns. A lack of product expertise can lead to missed opportunities and customer dissatisfaction.
Last but not least, short-term gains from aggressive upselling can be counter-productive in the long run. Pushing customers into products or services that don’t truly meet their needs can lead to dissatisfaction, decreased loyalty, and lower CLTV. Remember: building long-term relationships through thoughtful upselling is way more beneficial for the business.
In some cases, upselling customers to a higher-tier product or service might reduce the likelihood of repeat purchases. For example, if a customer purchases a high-end product with all the desired features, they may have no need for further upgrades or additions. That being said, it’s essential to balance the immediate benefits of upselling with the potential impact on future sales.
How Do I Implement Upselling and Cross-Selling?
We’ve got an answer: Zendesk! But let’s first examine how firms use its software for both upselling and cross-selling.
As we already discussed, upgrade suggestions have everything it takes to boost income. The caveat is that they need to be timed strategically. With user behavior tracked, you can locate moments when an upgrade aligns with a customer’s needs. For instance, if a user attempts to access a premium feature on a basic plan, a subtle prompt to upgrade can convert intent into action. New York-based UPSTACK leverages this strategy, using customer data and behavior to pinpoint upsell opportunities. The results are nothing short of amazing: annual revenue, doubled.
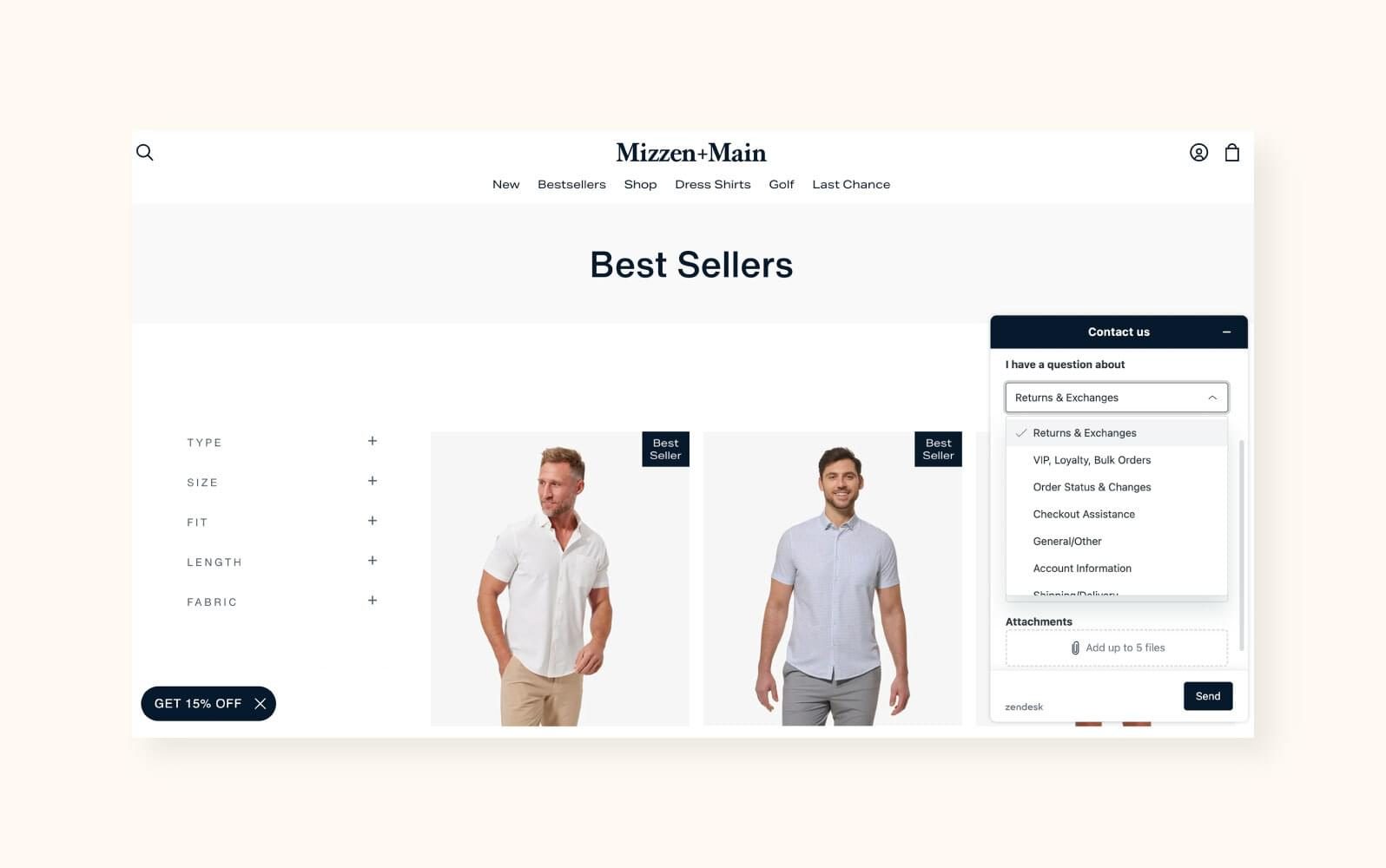
Enter Mizzen+Main. The menswear retailer provides its agents with a comprehensive view of each customer, including purchase history, sizing preferences, and order status. This rich data empowers agents to offer personalized recommendations, suggesting complementary items that align with customers’ tastes and needs.
Part of the Zendesk license making this all possible is called Zendesk Sell. Some quick stats:
- Two out of every three sales teams report a positive return on investment (ROI) within the first six months of implementation.
- More than half of all organizations experience double-digit revenue growth.
Cloudfresh is a Zendesk consultant that can help you put an end to the cross-sell vs. upsell debate by adopting this solution.
On top of that, we provide the following services:
- In-Depth Audit & Consulting.
- Full-Fledged Implementation.
- Third-Party Integrations.
- Employee Onboarding & Training.
- AI Support.
To get started, please fill out the form below.