Product Development Process: How to develop a product in 6 stages
Critical Path Method: How It Influences the Project Management Process
- What Is the Critical Path Method, and Why Use It?

- How to Find a Critical Path?

- An Example of a CPM
- How to Use the CPM?

- What Do We Offer?
Working on a project requires a lot of technology that helps you succeed with your results. One necessary technique is a critical path method, which allows you to visualize your project roadmap and prioritize essential tasks that need to be done. It is part and parcel of different project management strategies.
This blog will deeply analyze how the critical path method can help you manage your task dependencies, timeframes, and teamwork.
What Is the Critical Path Method, and Why Use It?
The CPM method was developed in the late 1950s to respond to the increased costs due to inefficient scheduling. Since then, it has become a popular project management technique for identifying activities needed to complete projects and determining their schedule. As the tasks are key to the project timeline, any delay in their execution will influence the rest of the project.
What Is a Critical Path in Project Management?
A critical path is the longest sequence of tasks in a project that must be completed on time for the entire project to finish on schedule. Any delays in these tasks will delay the entire project. It’s like the backbone of your project timeline, highlighting the essential tasks and their dependencies.
This technique can influence your project management results in various ways:
- Improve future planning. CPM can be used to measure your actual results against expectations so that you can use the data for future planning according to your experience.
- Facilitate the process of planning and scheduling your team’s resources and activities. With this technique, you can easily prioritize tasks and deploy resources more efficiently.
- Help avoid bottlenecks by showing you the dependencies among different tasks and enabling you to keep the activities in sync.
How to Find a Critical Path?
Here are six steps you should follow to find your critical path.
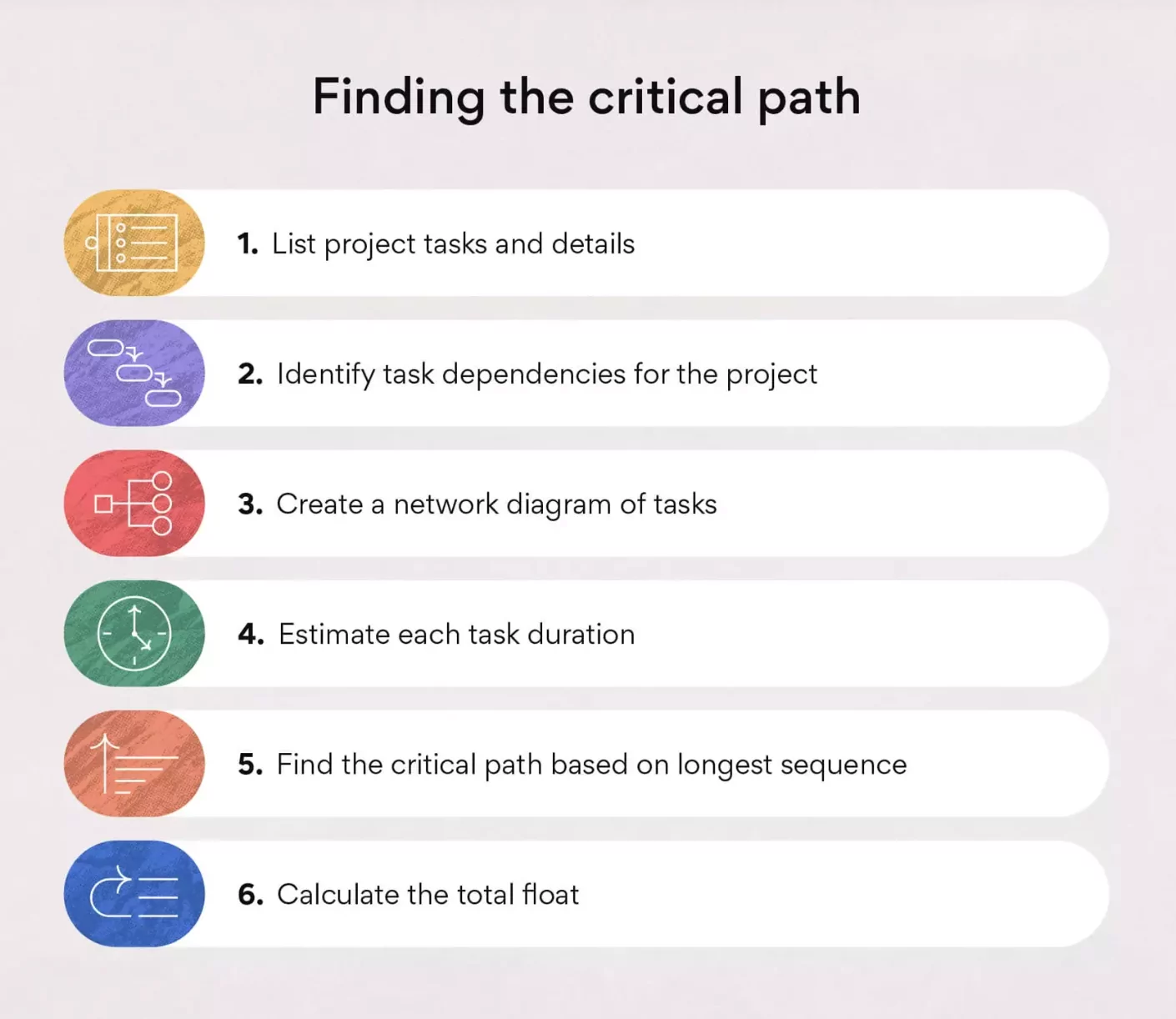
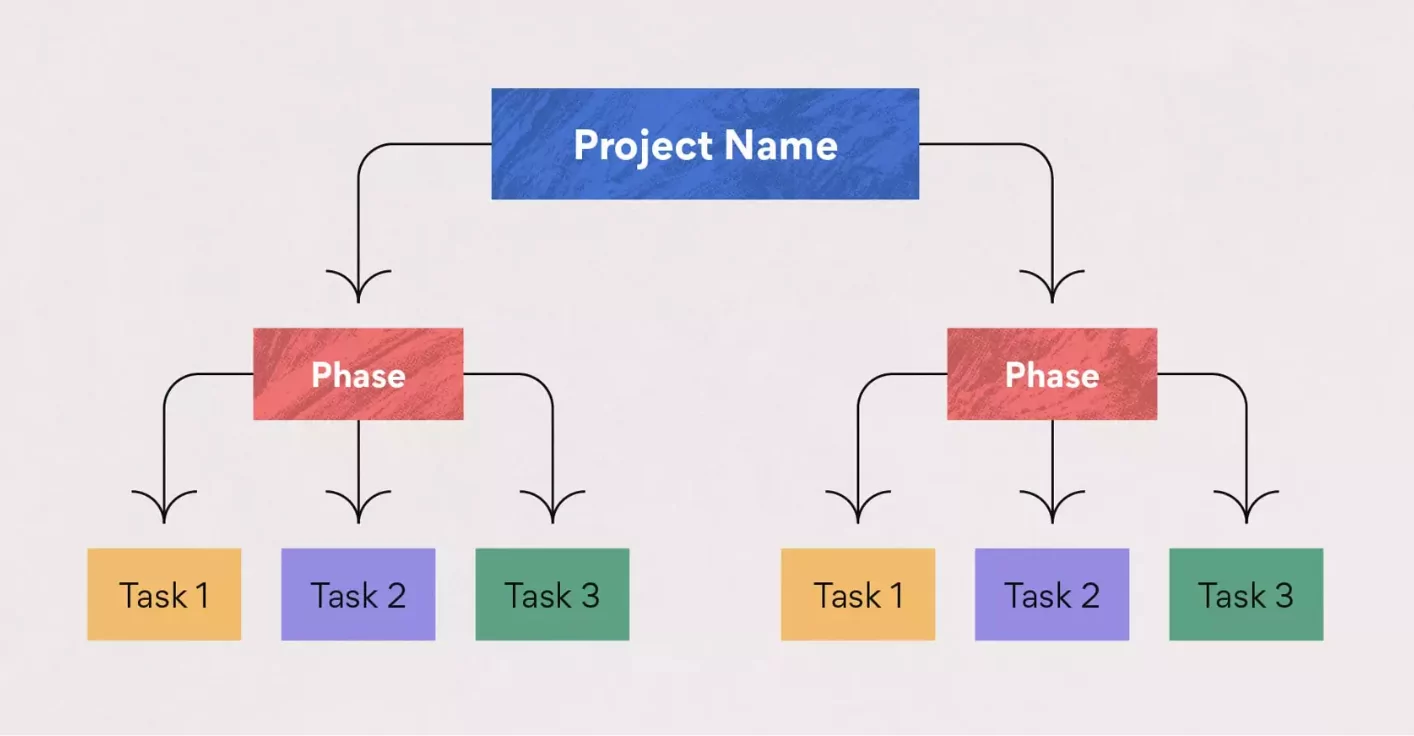
1. Use a Work Breakdown Structure
It is a tool that helps you organize your project by hierarchy and view critical dependencies among tasks by listing all the tasks required to proceed with your project. It is the foundation of your CPM. Once you have everything that needs to be done on board, you can start identifying task dependencies.
2. Identify Your Dependencies
Now you can spot tasks that depend on one another based on your breakdown structure. At this stage, you can also locate tasks that could be done in parallel.
3. Create Network Diagram
In this step, you should turn your breakdown structure into a network diagram putting tasks in each box chronologically and using arrows to depict task dependencies.
4. Estimate Task Duration
It is the task duration that you can estimate based on your experience and knowledge of previous project data or industry standards. The Asana team also recommends using the forward pass and backward pass technique.
- The forward pass is used to calculate early start (ES) and early finish (EF) dates by using a previously specified start date. The calculation starts with 0 at the ES of the first activity and proceeds through the schedule. This technique allows for the early allocation of resources to the project.
- A backward pass is used to calculate late start (LS) and late finish (LF) dates. The calculation starts with the last scheduled activity and proceeds backward through the entire schedule.
These two techniques can also be used to determine each task’s float or scheduling flexibility.
5. Calculate the Critical Path
For calculating your critical path manually, the first step is to write down the start and end times next to each activity. For example, the beginning of the first activity is a 0, when the end time is the duration of this activity. The next activity you identified with your breakdown structure starts at the end time of the first activity (if they can not be done in parallel). The same logic remains for all the activities you mentioned as crucial to completing the project. In the end, you will have lots of different sequences of tasks.
Then, it would help if you determined the duration of the entire sequence by analyzing the time you put into the tasks. The most extended sequence of activities is your critical path. Once you have it, you can build the project schedule according to your critical path.
Here’s what the critical path diagram might look like:
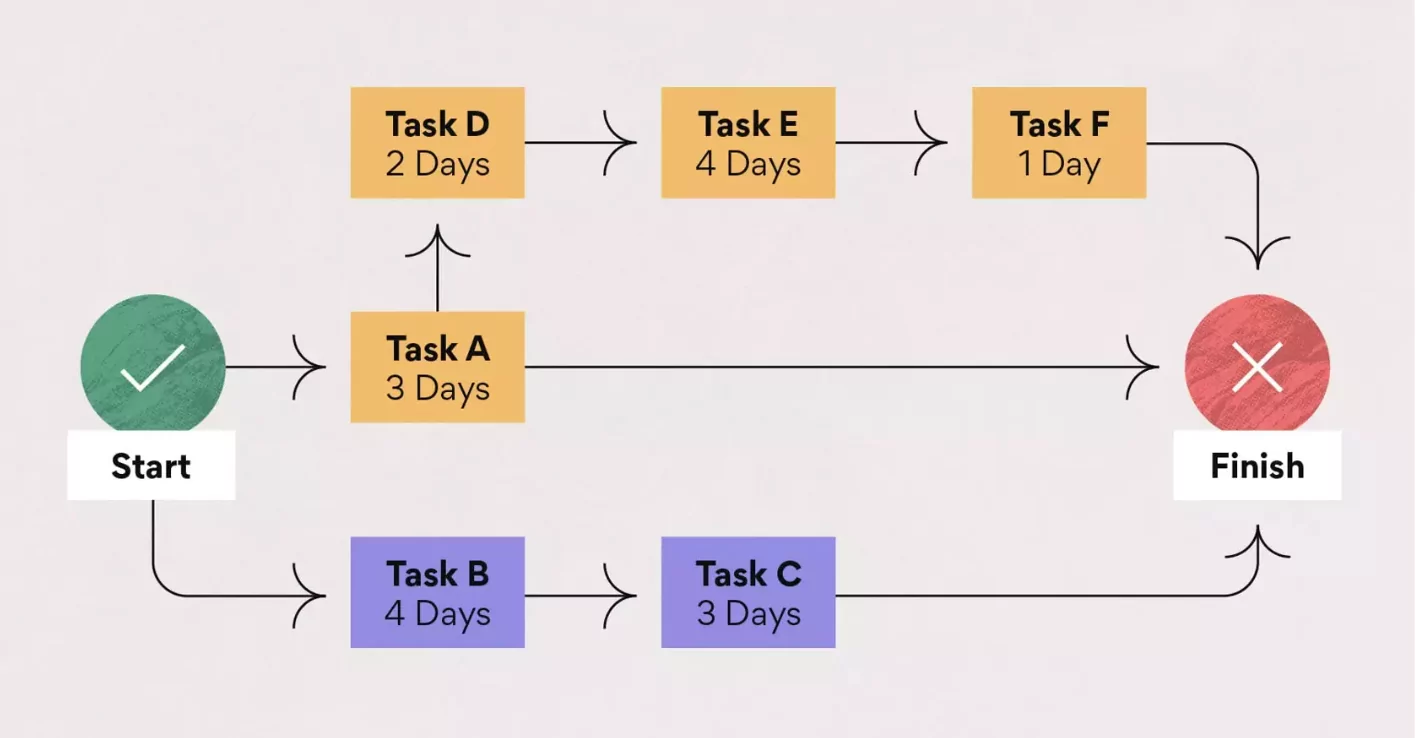
6. Calculate the Float
If you want to find out how much the task can be delayed without impacting subsequent tasks or the project end date, calculate the float, which refers to your tasks’ flexibility. It is a crucial resource covering project management risks or unexpected issues.
Remember that your critical tasks always have zero floats. Only the tasks besides your critical path could be delayed without affecting the project completion date.
Calculating the float can be done with an algorithm or manually. Use the calculations from the section below to determine the total float and the free float.
- Total float: This is the amount of time an activity can be delayed from the early start date without influencing the project finish date. To calculate the total float, you should extract your Early Start from Late Start or your Early Finish from the Late Finish.
- Free float: This is the amount of time your activity can be delayed without influencing your further activity. To calculate the free float, you should extract the Early Finish of your current task from the Early Start of your next task.
Project managers can benefit from float calculation in several ways:
- It keeps your project schedule on track. The more flexible you are, the more chances you have to finish earlier or on time.
- It helps you prioritize your tasks by identifying the activities with free float and postponing some tasks with high flexibility.
- As we already mentioned, the float can also enable you to cover your project risks or unexpected issues that come up.
An Example of a CPM
Imagine an established investment bank looking to set up a crypto arm. What would a critical path look like in this scenario?
Hypothetically, activities and dependencies would be as follows:
- Regulatory Compliance (A): Getting necessary licenses and approvals from relevant authorities.
- Technology Infrastructure (B): Building or acquiring a secure trading platform and wallet infrastructure.
- Risk Management Framework (C): Coming up with an all-round risk management plan, including cybersecurity measures.
- Talent Acquisition (D): Hiring experienced professionals in crypto trading, blockchain technology, and compliance.
- Product Development (E): Designing and developing the trading platform interface and features, along with integrating those with external systems.
- Marketing and Sales (F): Crafting marketing materials and launching campaigns to attract clients.
Assume the following durations for the activities:
- Regulatory Compliance (A): 6 months
- Technology Infrastructure (B): 8 months
- Risk Management Framework (C): 2 months
- Talent Acquisition (D): 3 months
- Product Development (E): 4 months
- Marketing and Sales (F): 2 months
Calculating the critical path:
- Sequence 1: A → B → C → D → E → F: 6 + 8 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 2 = 25 months
- Sequence 2: A → B → C → E → F: 6 + 8 + 2 + 4 + 2 = 22 months
So in our hypothetical scenario, the critical path would be Sequence 1 (A → B → C → D → E → F) with a total duration of 25 months.
This sequence shows the most critical path for launching the crypto arm. It includes all necessary activities in a sequential order, a delay in any of which would directly impact the overall project timeline.
An alternative sequence (2) would give some space to parallel processing between activities D (Talent Acquisition) and E (Product Development), meaning those could be carried out simultaneously, potentially shortening project duration.
How to Use the CPM?
The CPM allows you to respond more confidently to issues and challenges you may encounter during your project, providing a swift reaction and eventually meeting the deadline.
1. Compress Schedules
Given that project deadlines may be brought forward, knowledge of CPM empowers you to use two schedule compression techniques: fast-tracking and crashing. During fast-tracking, you identify the activities that could be done simultaneously and run them in parallel, speeding up your project duration. Meanwhile, in the crashing technique, you should allocate more resources to accelerate your activities but also approve the project scope with your stakeholders.
2. Resolve Resources Shortage
Suppose, for example, that your project bumps into the resource issue. In such a case, some team members end up overloaded, or the need arises for additional equipment. You should use the resource leveling technique that involves resolving overallocation or scheduling conflicts to ensure a project can be completed with the available resources. With this technique, you will adjust your project start and end dates and keep in mind that you may need to readjust your critical path.
3. Collect Data for Future Use
As your project runs, you can always compare your expectations with the reality—e.g., the original critical path to the actual critical path—and use this data as a reference to make more relevant and accurate estimations about your future projects.
As we have seen, the critical path method in project management can help visualize project workflows better and keep everything under control, from the time and schedule to different tasks that could be postponed or are key to project completion. All these could be tracked through Asana, one of the most popular project management tools.
How to Calculate the Critical Path in Project Management?
There are different methods, but a common approach involves:
- Listing all project tasks.
- Identifying dependencies among tasks (which task needs to be done before another can start).
- Estimating task durations.
- Using software or a network diagram to visualize the task sequence and dependencies.
- Analyzing the diagram to identify the longest path without slack (buffer time).
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the product development process, you can read more about its stages, techniques, and best practices in our article.
Enhance your decision-making arsenal by understanding how a decision matrix works—it’s a game-changer for breaking down complex scenarios into manageable pieces.
If you want to learn more about Asana, reach out to Cloudfresh Asana experts.
What Do We Offer?
- Implementation (Asana AI included). Helping you understand the process and answer all your questions.
- Migration. Developing our tools for migration if needed.
- Deployment. Helping you get a smooth start with the product.
- Audit and consulting. Providing two types of training: for users and administrators.
- Development of integrations with other systems. Adjusting to other systems you use.
- Technical support: Resolving all the incidents on Asana, requests for the correct use of services, etc.
By cooperating with Cloudfresh, you additionally receive the following:
- Payment by invoice in EUR, USD, CZK, PLN, UAH, or cryptocurrency.
- Collaboration in your native language thanks to the multilingualism of our team.
- Extensive professional support throughout using the services.
Contact our team to improve your organization’s IT infrastructure and take your project management experience to the next level with Asana solutions.