How to Choose the Best Security Questions for Maximum Safety
What Is OTP Authentication?
- SMS
- Authenticator Applications

- Hardware
- What Is OTP’s Value for Business?
- About Us
OTPs, also known as one-time passwords or one-time passcodes, are a measure that makes user accounts better secured. OTPs are nothing like traditional passwords — which are static — but unique sets of digits and/or characters generated randomly for just one use. So, even if a hacker were to intercept an OTP, it would turn useless quite quickly.
The delivery typically happens via secure channels like SMS, e-mail, or an authenticator app. After the user gets the code, they enter it into the sign-in form. If the OTP matches the system-generated one, they’re in. Requiring both the user’s knowledge (password) and possession (OTP), such a mechanism makes it much easier to battle illicit access attempts.
So, what is an OTP code, and how does OTP work?
SMS
While it’s true that SMS-based OTPs are super-user-friendly and widely accessible, they come with their own drawbacks. One such drawback is the vulnerability to SIM swapping attacks. In a nutshell, malicious actors sometimes trick mobile carriers into moving a phone number to a new SIM card and disabling the old one. The goal is to gain control of all the OTPs sent to that number, which can put the victim’s accounts at a huge risk if they stay unaware of the SIM swap and don’t react in time.
Another concern is that SMS delivery can be rather unreliable in some situations — think of network congestion, technical issues, or carrier delays. All these can cause SMS messages to arrive later or not arrive at all. OTP-wise, that means the user won’t be able to authenticate and will be left frustrated.
E-mail is another highly adopted channel for distributing OTPs. They can come either as codes or so-called ‘magic’ links — the latter are used by the likes of Medium and Slack. The most significant concern here is the vulnerability to phishing attacks. So what these scams do is target e-mail accounts to deceive users into clicking on malicious links or downloading malware-riddled attachments. If a user falls victim to phishing, they may unintentionally reveal their OTP to an intruder and leave their account security compromised.
To mitigate this risk, users should be educated on how to stay alert, avoid clicking on suspicious links, and consider using alternative methods (authenticator apps or hardware tokens, to name a few).
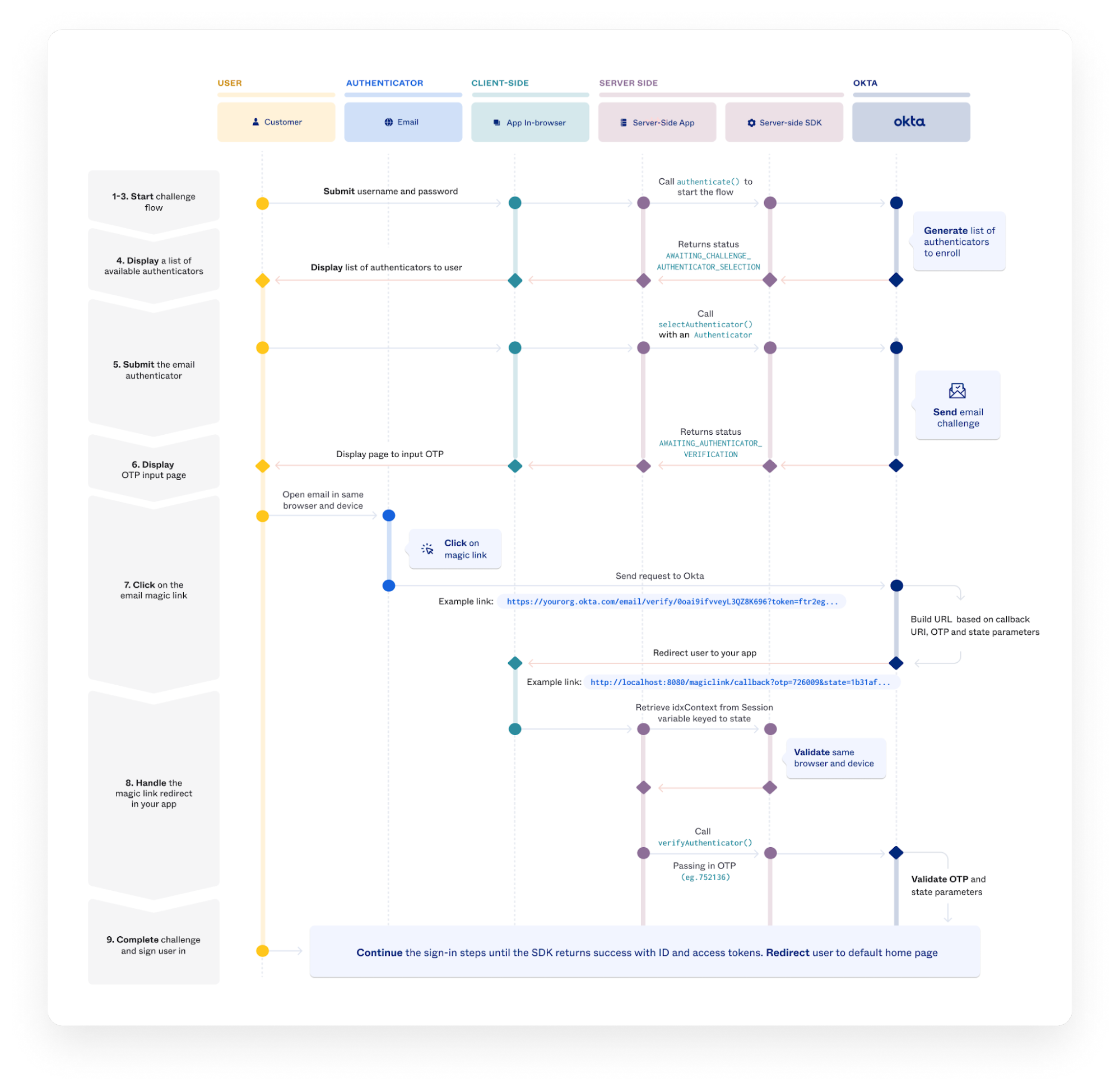
This diagram shows how to implement OTP authentication using Java.
Source: developer.okta.com
Authenticator Applications
Auth apps are a more secure alternative to SMS and email-based OTPs. They produce unique codes locally based on a time-synchronized clock, making them way less susceptible to various attacks. Besides, users can get OTPs directly from their smartphones, meaning they won’t need to rely on an SMS, email, or even Internet services provider.
Because authenticator apps can be used on various devices, users can enjoy greater flexibility. There are several limitations, though. For one, the user must have a compatible device with the authenticator app installed, which, in some cases, can prove somewhat of a challenge. Apart from that, if the device is ever lost or stolen, the user can end up getting locked out of their accounts and still at risk of unauthorized access. Nevertheless, OTPs generated via authenticator apps (such as one offered as part of Okta products) are generally viewed as a more secure and handy option.
Recovery Codes
Speaking of lockout and data loss, recovery codes are a type of OTP that helps users access the account in case they’ve lost their authenticator app-hosting device. These codes are pre-generated and typically available on-demand upon sign-up. One can store them offline in a secure location for less vulnerability to online threats.
Of course, recovery codes have their own flaws. Users typically have a limited number of codes, which can be a concern if they are lost. Moreover, if one does not store recovery codes securely, they can be compromised, opening a path to unauthorized access if not re-generated in time. So, for a business, it’s essential to educate customers on how to handle recovery codes with care and safety.
Yes, recovery OTPs are a useful backup mechanism, but one should not rely upon them as the only means of protection. Instead, you should prompt your users to configure robust two-factor authentication (2FA) for ongoing security and consider recovery codes exclusively as a last resort.
Hardware
Hardware OTPs are physical and offer a greater level of protection compared to software-based OTPs. These devices generate high-refresh-rate unique codes offline, which makes them nearly immune to known attack vectors. Users may carry the hardware token with them, and what they get in return is a tangible layer of security and reduced risk of interception.
It shouldn’t come as a surprise that hardware OTPs have additional costs compared to software-based options. Users need to buy and carry a physical device around — which is, let’s be frank, quite far from convenient, especially if we talk about mobile users who may not always have their token at hand.
Despite these drawbacks, hardware OTPs prove immensely valuable to those who require a high level of security when handling sensitive data or dealing with high-risk environments.

What Is OTP’s Value for Business?
- For employees, enforcing OTPs via 2FA adds a strong protective layer to their corporate accounts, which helps safeguard sensitive information and build trust. The bottom line? Reduced risk of data breaches and disruptions to business operations and improved productivity and morale.
- For customers, the ability to opt for OTPs shows a commitment to privacy and can help prevent fraudulent transactions and financial losses. Thanks to OTP implementation, businesses can improve the overall CX and strengthen customer relationships by lowering the risk of account hijacking.
What’s really important here is that OTPs can make a work environment more positive and productive, as well as make relationships with your clientele long-lasting. All while shielding your business from reputational and financial damage followed by regulatory scrutiny!
About Us
Cloudfresh is an Okta Activate Partner with a product specialization in Workforce Identity Cloud (WIC). What we can implement specifically for you extends well beyond regular one-time-password solutions described in this article; one example is Adaptive Authentication, which factors in device information, location, and user behavior for each sign-in attempt. There’s more: Customer Identity and Access Management (What is CIAM?), Single Sign-On, Workflows, Lifecycle Management, Universal Directory, Advanced Server Access, Access Gateway, and API Access Management, to name a few.
To cut a long story short, however complex your security needs and requirements are, Cloudfresh’s certified professionals are capable of addressing them on time and on budget. If you’d like to hop on a quick call and share all the gains you’d like to achieve, don’t hesitate to fill out the short form below and book your Okta consulting session.